

While more than one limb is often tested in a single encounter, you will count “one” for each named muscle tested in each limb to get your total muscle count for that limb - the muscles tested in each limb are counted separately “by limb” and not calculated all together for purposes of EMG coding. complete, you need to determine how many muscles are tested in a “single limb” and decide if the EMG in that one limb is limited or complete. So to clarify this concept of limited vs. One common mistake I see coders make when counting muscles to determine if the EMG is limited or complete is counting all muscles tested in multiple limbs together and then concluding the EMG is complete. A complete EMG of the limb involves testing 5 or more muscles in a single limb.A limited EMG of the limb involves testing 4 or fewer muscles in a single limb.The next thing to know about EMGs of the limbs is that they may be either limited or complete.

We will look at our code options in detail in just a moment.
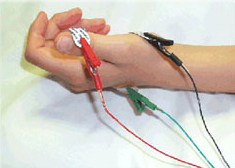
There are different codes for EMGs of the arms/legs when performed with an NCS when compared to EMGs performed by themselves without an NCS. Nerve conduction studies measure the speed at which nerves relay signals to the muscles they innervate (or communicate with). The first thing to know about EMG testing of the limbs is that it may be performed by itself or in conjunction with another test known as a nerve conduction study (NCS) during the same encounter. If you do have questions about coding EMGs of the head/neck/trunk muscles, head over to our “contact” page on our website to ask your question there or comment on this article, and I will be happy to assist with those additional questions. Our article today will focus on how to code EMGs of the limb muscles since these procedures are so commonly performed. An EMG test can be useful in diagnosing disorders of the muscles or nerves that provide electrical signals to those muscles including conditions such as carpel tunnel syndrome, multiple sclerosis (MS), and muscular dystrophy.Īn EMG is most commonly performed on muscles in the arms and legs (also known as the “limb muscles”), but may be performed on muscles of the head, neck, and trunk as well. The goal of the EMG is to confirm if muscle activity is normal or if there are abnormalities which indicate a disease/disorder of the muscles. The physician uses special equipment to listen to and/or visualize the muscle activity. During an EMG, small needle electrodes are passed through the skin and into the muscles being tested to measure the electrical activity of the muscles as patients are asked to contract and relax the muscle being tested. An electromyogram (or EMG) is a test commonly performed by neurologists to test the health and electrical response of the muscles.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
